Il packaging farmaceutico svolge un ruolo fondamentale nella protezione dei farmaci, mantenendone l'efficacia e garantendo la sicurezza dei pazienti. Che siate un produttore farmaceutico, un'azienda di integratori o un fornitore di packaging, in questa guida scoprirete le principali tipologie di packaging farmaceutico, i materiali utilizzati, i macchinari impiegati e le tendenze che plasmano il futuro del packaging farmaceutico.
Il packaging farmaceutico si riferisce al processo di confezionamento di prodotti farmaceutici, come compresse, capsule, liquidi, polveri o iniettabili, in contenitori che ne garantiscono la sicurezza, la stabilità e la fruibilità, dalla produzione al consumo finale. Il packaging farmaceutico comprende un'ampia gamma di tipologie, materiali e tecnologie di confezionamento, progettati per molteplici scopi.
Funzioni chiave del confezionamento farmaceutico:
• Protezione: Protegge il prodotto da danni fisici, contaminazione microbica, luce UV, umidità e ossigeno.
• Conservazione: Aiuta a mantenere la stabilità chimica e fisica del farmaco durante lo stoccaggio o il trasporto.
• Identificazione: Visualizza dettagli essenziali quali il nome del farmaco, il dosaggio, il numero di lotto, la data di scadenza, il produttore, ecc.
• Sicurezza e conformità del paziente: Garantisce facilità d'uso, dosaggio accurato e caratteristiche antimanomissione per prevenire usi impropri.
• Conformità normativa: Soddisfa i requisiti GMP, di serializzazione e di etichettatura per la distribuzione globale.
Gli imballaggi farmaceutici possono essere suddivisi in tre categorie principali: imballaggio primario, secondario e terziario; ciascuna tecnologia di imballaggio ha uno scopo specifico nella filiera farmaceutica.
L'imballaggio primario è il primo strato di imballaggio farmaceutico a diretto contatto con prodotti come pillole, compresse, capsule, ecc. È essenziale per preservare la stabilità del farmaco ed evitare contaminazioni. Questo tipo di imballaggio farmaceutico deve soddisfare rigorosi standard qualitativi. GMP (Buone pratiche di fabbricazione) e le linee guida FDA/EMA.
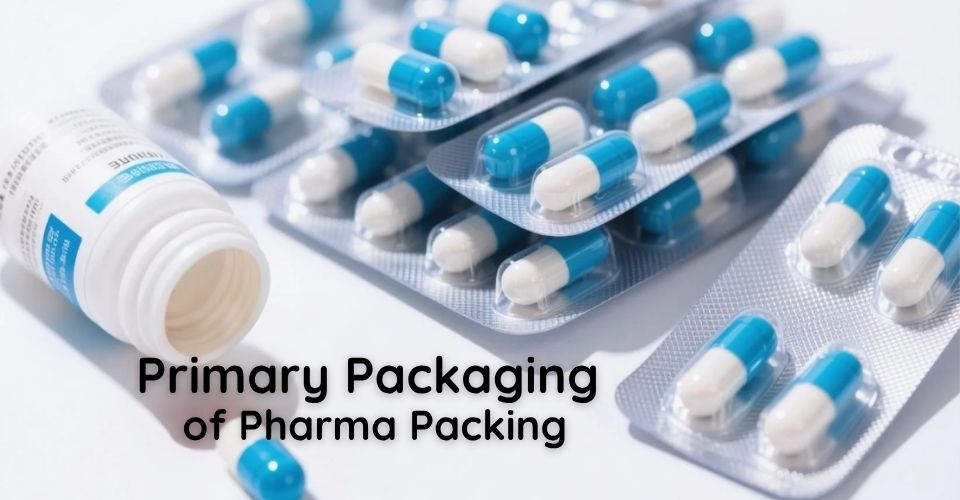
Esempi comuni di imballaggio farmaceutico primario includono:
• Blister per compresse e capsule.
• Bottiglie di plastica o di vetro per sciroppi liquidi o dosi solide.
• Fiale e fiale per iniettabili.
• Bustine e bustine per polveri e dosi monouso.
Il packaging secondario per l'industria farmaceutica è lo strato esterno che contiene uno o più contenitori primari. È fondamentale per il branding, l'etichettatura, le informazioni per i pazienti e la sicurezza antimanomissione. Sebbene non entri in contatto diretto con il prodotto, è essenziale per la conformità normativa e la fiducia dei consumatori.
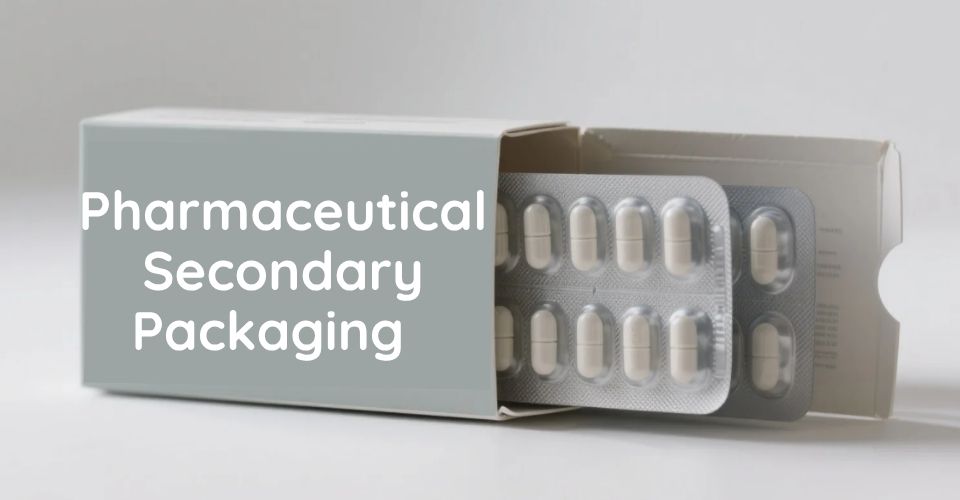
I formati tipici di confezionamento farmaceutico secondario includono:
• Involucri fluidi
• Scatole di cartone
• Scatole stampate con inserti prodotto
• Fasci termoretraibili
Gli imballaggi secondari spesso contengono informazioni importanti, come istruzioni sul dosaggio, numeri di lotto e date di scadenza, a supporto della tracciabilità farmaceutica e della sicurezza del paziente.
3) Confezionamento terziario di prodotti farmaceutici
L'imballaggio terziario è progettato per la movimentazione, la spedizione e la logistica di grandi quantità di prodotti farmaceutici. Garantisce che i prodotti farmaceutici raggiungano ospedali, farmacie e distributori intatti e senza danni durante il trasporto.

Esempi di confezionamento farmaceutico terziario:
• Scatole di cartone ondulato per la spedizione
• Pallet in legno o plastica
• Contenitori e casse sfuse
Questo strato di imballaggio è particolarmente importante per la logistica della catena del freddo, in particolare per i farmaci sensibili alla temperatura, come vaccini e prodotti biologici.
Il packaging farmaceutico è ampiamente utilizzato nel settore, ma sai quali sono i 5 tipi di packaging farmaceutico più diffusi?
I blister sono tra le soluzioni di confezionamento primario più comunemente utilizzate nell'industria farmaceutica. Sono costituiti da una cavità preformata in plastica sigillata con un supporto in alluminio o in pellicola di plastica. Ogni tasca contiene una dose singola, contribuendo a proteggere dall'umidità e dall'ossidazione, a migliorare la compliance del paziente con il confezionamento monodose e a ridurre il rischio di contaminazione durante la manipolazione.
Ecco una breve tabella con le informazioni generali sul confezionamento in blister.
|
Caratteristica |
Descrizione |
|
Vantaggi |
- Controllo della dose unitaria - Elevata protezione barriera - Antimanomissione |
|
Applicazioni |
- Compresse Pillole - Capsule Pillole - Integratori alimentari |
|
Materiali utilizzati |
- PVC/Alu- Alu/Alu (formatura a freddo)- Pellicole laminate PVDC |
|
Macchine utilizzate |
- Macchina confezionatrice blister - Macchina termoformatrice |
|
Adattamento normativo |
Standard GMP, FDA, UE per il confezionamento farmaceutico |
I flaconi sono contenitori versatili utilizzati per liquidi orali, sciroppi, vitamine e dosi solide come capsule e compresse. Esistono due tipi principali di flaconi:
• Le bottiglie di plastica (solitamente HDPE o PET) sono leggere, resistenti agli urti e convenienti.
• Le bottiglie di vetro (spesso ambrate o trasparenti) offrono una resistenza chimica superiore e sono ideali per i farmaci sensibili alla luce.
Ecco una breve tabella con le informazioni generali sul confezionamento delle bottiglie.
|
Caratteristica |
Descrizione |
|
Vantaggi |
- Ideale per imballaggi sfusi - Richiudibile, antimanomissione - Facile erogazione |
|
Applicazioni |
- Capsule, compresse, capsule molli - Gommose e polveri - Sciroppi - Liquidi orali |
|
Materiali utilizzati |
- Bottiglie di plastica PET, HDPE - Bottiglie di vetro |
|
Macchine utilizzate |
- Macchina conta-compresse - Macchina tappatrice - Sigillatrice a induzione - Etichettatrice - Macchina riempitrice di liquidi (per liquidi orali e sciroppi, ecc.) |
|
Adattamento normativo |
Conforme a cGMP, FDA, HACCP per nutraceutici e farmaceutici |
Bustine e stick pack sono formati di imballaggio flessibili realizzati con film laminato che offrono una barriera protettiva contro umidità, ossigeno e raggi UV. Sono diffusi sia in ambito farmaceutico che nutraceutico per la loro praticità, trasportabilità e dosaggio accurato.

Ecco una tabella con le informazioni generali per le confezioni in bustina e stick pack.
|
Caratteristica |
Descrizione |
|
Vantaggi |
- Leggero, portatile, monodose - Eccellente protezione barriera - Forme personalizzabili (saldatura su 3 lati, saldatura su 4 lati, stick) - Conveniente per la produzione di massa - Ideale per un dosaggio preciso |
|
Applicazioni |
- Polveri nutraceutiche (collagene, probiotici) - Bevande elettrolitiche (ORS) - Caffè e tè istantanei - Enzimi, integratori a base di erbe - Creme, gel, miele e sciroppi |
|
Materiali utilizzati |
- Laminati multistrato PET/AL/PE - Carta/poliestere/lamina - Film termosaldabili |
|
Macchine utilizzate |
- Macchina confezionatrice verticale (VFFS) - Macchina per confezioni stick - Macchina confezionatrice per bustine (saldatura su 3/4 lati) - Macchina imballatrice multipista - Sistemi di dosaggio a coclea o volumetrici |
|
Adattamento normativo |
- cGMP, HACCP, FDA, ISO22000 (in particolare per alimenti e prodotti farmaceutici) - Supporta la codifica serializzata e la prova di manomissione |
|
Varianti comuni |
- Bustine con chiusura a 3 lati - Bustine con chiusura a 4 lati - Bustine con sigillo posteriore - Bastoncini con sigillo centrale - Pacchi a doppia camera o a doppio stick |

Ecco le informazioni relative al confezionamento a strisce in termini di vantaggi, applicazioni, ecc.
|
Caratteristica |
Dettagli |
|
Vantaggi |
- Ermetico, a prova di manomissione - Dimensioni compatte - Maggiore durata di conservazione |
|
Applicazioni |
Compresse, pastiglie, masticabili |
|
Materiali utilizzati |
- Foglio di alluminio - Pellicola di carta-alluminio-polietilene - Composito PE/Alu |
|
Macchine utilizzate |
Macchina imballatrice a strisce |
|
Approfondimenti chiave |
Spesso utilizzato per formulazioni pediatriche o sensibili all'umidità |
Utilizzate principalmente per farmaci iniettabili, vaccini e prodotti biologici, fiale e ampolle sono essenziali per il confezionamento sterile dei prodotti farmaceutici.
• Le fiale sono piccoli contenitori cilindrici con tappo in gomma e sigillo in alluminio. Disponibili sia in formato monodose che multidose, ideali per la ricostituzione.
• Le fiale sono contenitori di vetro sigillati progettati per essere aperti mediante rottura. Offrono una protezione straordinaria contro la contaminazione e l'esposizione all'aria.

Ecco una tabella con le informazioni generali su fiale e ampolle.
|
Caratteristica |
Dettagli |
|
Vantaggi |
- Ideale per iniettabili - Elevata sterilità e barriera - A prova di manomissione |
|
Applicazioni |
Vaccini, insulina, antibiotici, colliri |
|
Materiali utilizzati |
Vetro di tipo I, plastica (COP/COC), tappi di gomma, capsule a crimpare in alluminio |
|
Macchine utilizzate |
- Linea di riempimento fiale (riempitrice + tappo + crimpatrice) - Macchina per il riempimento e la sigillatura di fiale |
|
Approfondimenti chiave |
Le fiale utilizzano tappo + crimpatura; le ampolle sono tubi di vetro sigillati a fiamma |
Scegliere il giusto packaging farmaceutico è essenziale per mantenere la stabilità della pillola, soddisfare le normative e garantire la sicurezza del paziente. Con così tanti formati come blister, flaconi, fiale e bustine, è importante abbinare il prodotto al packaging giusto in base alla sua forma, sensibilità, mercato di riferimento ed esigenze di produzione.
La tabella seguente aiuta a semplificare questa decisione confrontando fattori chiave come applicazioni, vantaggi e macchinari compatibili.
|
Criteri |
Dettagli |
Esempi / Tipi di imballaggio |
|
1. Forma di dosaggio |
Adattare l'imballaggio alla forma fisica del prodotto. |
- Compresse: Blister, Flacone, Striscia - Liquidi: Bottiglia, Fiala, Ampolla - Polveri: Bustina, stick pack |
|
2. Sensibilità del prodotto |
Prendi in considerazione la protezione da umidità, luce e ossigeno. |
- Sensibile all'umidità: Blister in alluminio-alluminio, imballaggio a strisce - Sensibile alla luce: Bottiglia ambrata, sacchetto di alluminio |
|
3. Aderenza del paziente |
Assicurarsi che la confezione sia facile da aprire, dosare e conservare, soprattutto per anziani e bambini. |
- Bottiglie facili da aprire - Blister/striscia monodose - Confezioni calendario per uso quotidiano |
|
4. Conformità normativa |
Gli imballaggi devono soddisfare le normative specifiche del Paese (ad esempio FDA, EMA, GMP) e spesso includono prove di manomissione e serializzazione. |
- Tappi a prova di bambino - Sigilli antimanomissione - Etichette serializzate |
|
5. Mercato di riferimento |
Considerare l'aspetto della confezione, la sua trasportabilità e la facilità di distribuzione, soprattutto in caso di vendita al dettaglio o esportazione. |
- Confezione Schet & Stick per utenti in movimento - Bottiglie per scaffali di vendita al dettaglio - Confezionamento blister per ospedali |
|
6. Requisiti di durata di conservazione |
Scegli materiali ad alta barriera per una maggiore durata di conservazione o API instabili. |
- Confezionamento blister Alu-Alu - Film multistrato per bustine - Fiale di vetro con tappi di gomma |
|
7. Scala di produzione |
Adatta il formato dell'imballaggio al volume di produzione e all'efficienza della linea. |
- Vescica: velocità medio-alta - Bottiglie: riempimento rapido e sfuso - Bustine: efficiente per le polveri |
|
8. Considerazioni sui costi |
Equilibrio tra costo dei materiali, investimento nei macchinari e spesa per imballaggio unitario. |
- Bottiglie: costi dei materiali più elevati, manodopera ridotta - Confezioni stick: basso costo del materiale per unità |
|
Tipo di imballaggio |
Macchine richieste |
|
Confezionamento in blister |
Macchina confezionatrice blister (alluminio-PVC, alluminio-alluminio, carta-PVC) |
|
Imballaggio in flacone per compresse |
Disordinatore di bottiglie, macchina conta-compresse, tappatrice, macchina sigillatrice a induzione, etichettatrice |
|
Confezionamento in bustina/stick |
Macchina confezionatrice verticale (multipista) |
|
Confezionamento a strisce |
Macchina imballatrice a strisce |
|
Confezionamento di fiale/ampolle |
Macchina per il riempimento di liquidi, macchina per tappatura o sigillatura a fiamma, sterilizzatore, crimpatrice per tappi |
Scegliere un fornitore affidabile di packaging farmaceutico è molto importante per molteplici motivi. Che si tratti di reperire materiali di confezionamento primario (come blister, flaconi o fiale) o di cercare soluzioni complete per il packaging farmaceutico, queste aziende affidabili offrono una comprovata esperienza nel settore farmaceutico.
|
Fornitore/ Produttore |
Paese |
Specialità |
Perché sceglierli |
|
Schott AG |
Germania |
Fiale di vetro, ampolle, cartucce, siringhe |
Leader nel settore del vetro farmaceutico ad alta purezza e degli imballaggi iniettabili. |
|
Gerresheimer |
Germania |
Imballaggi in vetro e plastica, fiale, siringhe preriempite |
Forte presenza globale e competenza nel confezionamento di prodotti biologici. |
|
Farmaceutica occidentale |
U.S.A. |
Tappi in gomma, guarnizioni, sistemi di componenti iniettabili |
Affidabile per i componenti di imballaggio iniettabili e l'integrità della chiusura del contenitore. |
|
Cina |
Macchine per il confezionamento in blister, riempimento di capsule, contatrici di compresse, linee di imbottigliamento per il conteggio di compresse e capsule. |
Soluzione completa per macchine automatiche per il confezionamento farmaceutico, con assistenza locale disponibile. |
|
|
Cina |
Confezionamento in blister, Macchine contatrici di compresse, macchine confezionatrici di bustine, ecc. |
Specializzati in linee di confezionamento personalizzate per integratori e prodotti farmaceutici, con supporto in loco a livello globale. |
|
|
Cina |
Macchine blisteratrici, confezionamento di capsule molli, conteggio e riempimento di capsule e compresse. |
Macchinari convenienti con supporto globale per produttori su piccola e grande scala. |
|
|
Origin Pharma |
Regno Unito |
Materiali di imballaggio primario, soluzioni di progettazione e approvvigionamento |
Ideale per startup e sviluppatori di formulazioni che necessitano di un supporto agile per il packaging. |
Il confezionamento in blister è uno dei formati più utilizzati grazie all'eccellente protezione, alla facilità d'uso e alla possibilità di dosare il prodotto singolarmente. È particolarmente apprezzato per compresse e capsule.
• L'imballaggio primario è a diretto contatto con il farmaco (ad esempio blister, flacone, fiala).
• L'imballaggio secondario è lo strato esterno che contiene e protegge l'imballaggio primario (ad esempio, cartoni, scatole).
Le confezioni blister e le bottiglie in vetro ambrato sono ideali per i prodotti sensibili all'umidità, poiché offrono una protezione barriera superiore.
Sì, entrambi i formati sono ampiamente utilizzati per polveri, granuli e sali reidratanti orali. Sono comodi, portatili e ideali per dosi singole.